
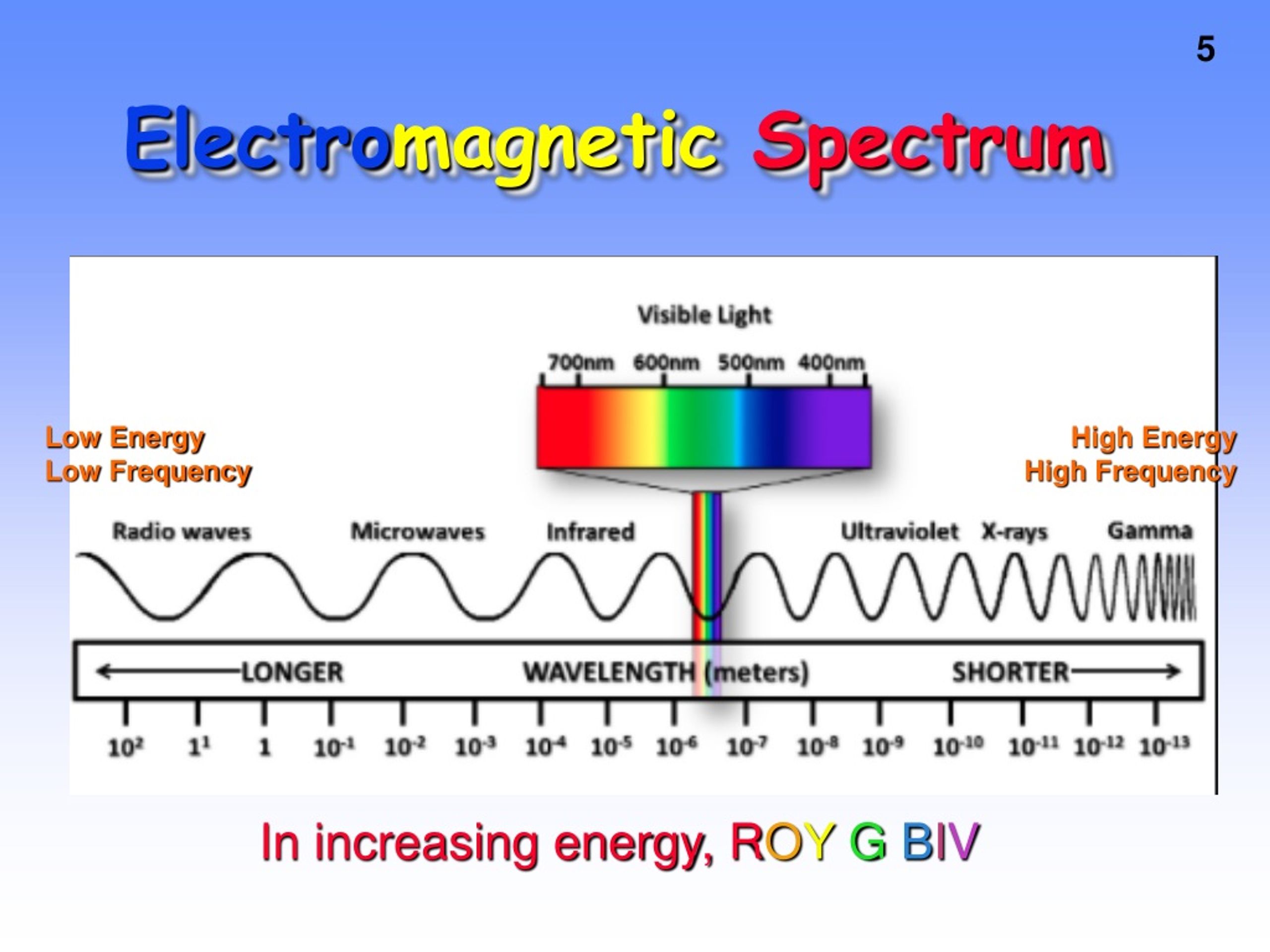
When talking about electromagnetic waves, we can refer either to wavelength or to frequency - the two values are interconverted using the simple expression: Frequency is commonly reported in hertz (Hz), meaning ‘cycles per second’, or ‘waves per second’. Longer waves have lower frequencies, and shorter waves have higher frequencies. Where E is energy in J, λ (the Greek letter lambda) is wavelength in meters, c is 3.00 x 10 8 m/s (the speed of light), and h is 6.626 × 10 −34 J īecause electromagnetic radiation travels at a constant speed, each wavelength corresponds to a given frequency, which is the number of times per second that a crest passes a given point.

If we describe light as a stream of photons, the energy of a particular wavelength can be expressed as: (Recall the concept known as ‘wave-particle duality’: at the quantum level, wave behavior and particle behavior become indistinguishable, and very small particles have an observable ‘wavelength’). The notion that electromagnetic radiation contains a quantifiable amount of energy can perhaps be better understood if we talk about light as a stream of particles, called photons, rather than as a wave. Remember, wavelength tells you the type of light and amplitude tells you about the intensity of the light. You can see this depicted in the image below. Wavelengths are important in that they tell one what type of wave one is dealing with. Shorter wavelength means greater frequency, and greater frequency means higher energy. This wavelength frequently relationship is characterized by: Consequently lead aprons are worn to protect our bodies from harmful radiation when we undergo x-rays. Shorter wavelength waves such as x-rays carry higher energy that can be hazardous to our health. Longer wavelength waves such as radio waves carry low energy this is why we can listen to the radio without any harmful consequences.
#Electromagnetic radiant energy examples full#
Wavelength (\(\lambda\)) is the distance of one full cycle of the oscillation (measured between the distance of either crest to crest as shown above or trough to trough).

The different properties of the various types of electromagnetic radiation are due to differences in their wavelengths, and the corresponding differences in their energies: shorter wavelengths correspond to higher energy. This energy is then grouped into categories based on its wavelength into the electromagnetic spectrum. For example, sound waves need either a gas, solid, or liquid to pass through in order to be heard. Most other types of waves must travel through some sort of substance.
This radiation can travel through empty space. Electron radiation is released as photons, which are bundles of light energy that travel at the speed of light as quantized harmonic waves. These electric and magnetic waves travel at 90 degree angles to each other and have certain characteristics, including amplitude, wavelength, and frequency. Electromagnetic radiation, as you may recall from a previous chemistry or physics class, is composed of electrical and magnetic waves which oscillate on perpendicular planes as shown in the diagram below. Light, electricity, and magnetism are all different forms of electromagnetic radiation. Make certain that you can define, and use in context, the key terms below.Īs you read the print off this computer screen now, you are reading pages of fluctuating energy and magnetic fields.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
